Liquid Oxygen
Liquid Oxygen (LOX) is used as therapy for respiratory patients. Medical oxygen in liquid form offers several advantages over the other two oxygen therapy modes. These two modes consist of compressed oxygen and concentrated oxygen. Compressed oxygen is usually dispensed through oxygen cylinders or tanks while concentrated oxygen is offered by electrically powered concentrator machines. Liquid oxygen is stored and dispensed in the home by an oxyge

Advantages of Liquid Oxygen
Liquid oxygen is lightweight making it easier to carry than other oxygen alternatives. It lasts longer between refills, giving you more time to run errands or have fun. It provides 100% oxygen with better therapy outcomes. Both the home storage reservoir and the portable carry-a-long do not need a power source. Liquid oxygen offers both continuous flow and pulse flow oxygen. Portable units fully recharge in less than two minutes.
Summary of Advantages
- Offers 100% oxygen.
- Provides better therapy outcomes.
- Offers higher output of up to 15 liters per minute of oxygen flow.
- Provides longer supply duration of 5 to 14 hours longer.
- No sound emissions during operation.
- Very discreet oxygen therapy.
- No power source required.
- Lightweight and easy to carry.
- Short refill time of less than 2 minutes.
Basic Components of Home Liquid Oxygen

There are two basic components for home liquid oxygen. First is a home storage reservoir that is usually refilled every 2 weeks. This device supplies oxygen while the patient is at home and recharges the second component--the portable LOX unit. The portable carry-a-long is lightweight and provides oxygen for an extended period of time. At a setting of 2 liters per minute, the portable unit can provide oxygen for up to 18 hours. Combined, these two components offer an unparalleled oxygen therapy service that provides more patient freedom and a better lifestyle.
Chart Industries is the premier manufacturer in the United States for liquid oxygen therapy devices. Their most popular liquid oxygen brand is the HELiOS.
Product Video
Home Liquid Oxygen Therapy Equipment Video (1:20 minutes)
LOX therapy has been studied by medical professionals around the world and compared with compressed oxygen and concentrated oxygen in numerous studies. Below is a list of resources highlighting some of these studies.
Liquid Oxygen Medical Studies
-
 Tarpy, Stephen P., and Bartolome R. Celli. "Long-term oxygen therapy." New England Journal of Medicine 333.11 (1995): 710-714.
Tarpy, Stephen P., and Bartolome R. Celli. "Long-term oxygen therapy." New England Journal of Medicine 333.11 (1995): 710-714. -
 Nasilowski, Jacek, et al. "Comparing supplementary oxygen benefits from a portable oxygen concentrator and a liquid oxygen portable device during a walk test in COPD patients on long-term oxygen therapy." Respiratory medicine 102.7 (2008): 1021-1025.
Nasilowski, Jacek, et al. "Comparing supplementary oxygen benefits from a portable oxygen concentrator and a liquid oxygen portable device during a walk test in COPD patients on long-term oxygen therapy." Respiratory medicine 102.7 (2008): 1021-1025. -
 Krop, Harry D., A. Jay Block, and Edwin Cohen. "Neuropsychologic effects of continuous oxygen therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease."CHEST Journal 64.3 (1973): 317-322.
Krop, Harry D., A. Jay Block, and Edwin Cohen. "Neuropsychologic effects of continuous oxygen therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease."CHEST Journal 64.3 (1973): 317-322. -
 Pepin, Jean-Louis, et al. "Long-term oxygen therapy at home: compliance with medical prescription and effective use of therapy." CHEST Journal109.5 (1996): 1144-1150.
Pepin, Jean-Louis, et al. "Long-term oxygen therapy at home: compliance with medical prescription and effective use of therapy." CHEST Journal109.5 (1996): 1144-1150. -
 Eaton, T., et al. "Long-term oxygen therapy improves health-related quality of life." Respiratory medicine 98.4 (2004): 285-293.
Eaton, T., et al. "Long-term oxygen therapy improves health-related quality of life." Respiratory medicine 98.4 (2004): 285-293. -
 Vergeret, J., C. Brambilla, and L. Mounier. "Portable oxygen therapy: use and benefit in hypoxaemic COPD patients on long-term oxygen therapy."European Respiratory Journal 2.1 (1989): 20-25.
Vergeret, J., C. Brambilla, and L. Mounier. "Portable oxygen therapy: use and benefit in hypoxaemic COPD patients on long-term oxygen therapy."European Respiratory Journal 2.1 (1989): 20-25. -
 Petty, Thomas L., and Walter J. O'Donohue Jr. "Further recommendations for prescribing, reimbursement, technology development, and research in long-term oxygen therapy. Summary of the Fourth Oxygen Consensus Conference, Washington, DC, October 15-16, 1993." American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 150.3 (1994): 875-877.
Petty, Thomas L., and Walter J. O'Donohue Jr. "Further recommendations for prescribing, reimbursement, technology development, and research in long-term oxygen therapy. Summary of the Fourth Oxygen Consensus Conference, Washington, DC, October 15-16, 1993." American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 150.3 (1994): 875-877. -
 McDonald, C., A. Crockett, and I. Young. "Adult domiciliary oxygen therapy. Position statement of the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand."Medical Journal of Australia 182.12 (2005): 621-626.
McDonald, C., A. Crockett, and I. Young. "Adult domiciliary oxygen therapy. Position statement of the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand."Medical Journal of Australia 182.12 (2005): 621-626. -
 Howard, P., and R. De Haller. "Domiciliary oxygen--by liquid or concentrator? Working Group on Oxygen Therapy of IUATLD." European Respiratory Journal 4.10 (1991): 1284-1287.
Howard, P., and R. De Haller. "Domiciliary oxygen--by liquid or concentrator? Working Group on Oxygen Therapy of IUATLD." European Respiratory Journal 4.10 (1991): 1284-1287. -
 Lock, S. H., et al. "Comparison of liquid and gaseous oxygen for domiciliary portable use." Thorax 47.2 (1992): 98-100.
Lock, S. H., et al. "Comparison of liquid and gaseous oxygen for domiciliary portable use." Thorax 47.2 (1992): 98-100. -
 Ringbaek, T., P. Lange, and K. Viskum. "Compliance with LTOT and consumption of mobile oxygen." Respiratory medicine 93.5 (1999): 333-337.
Ringbaek, T., P. Lange, and K. Viskum. "Compliance with LTOT and consumption of mobile oxygen." Respiratory medicine 93.5 (1999): 333-337.
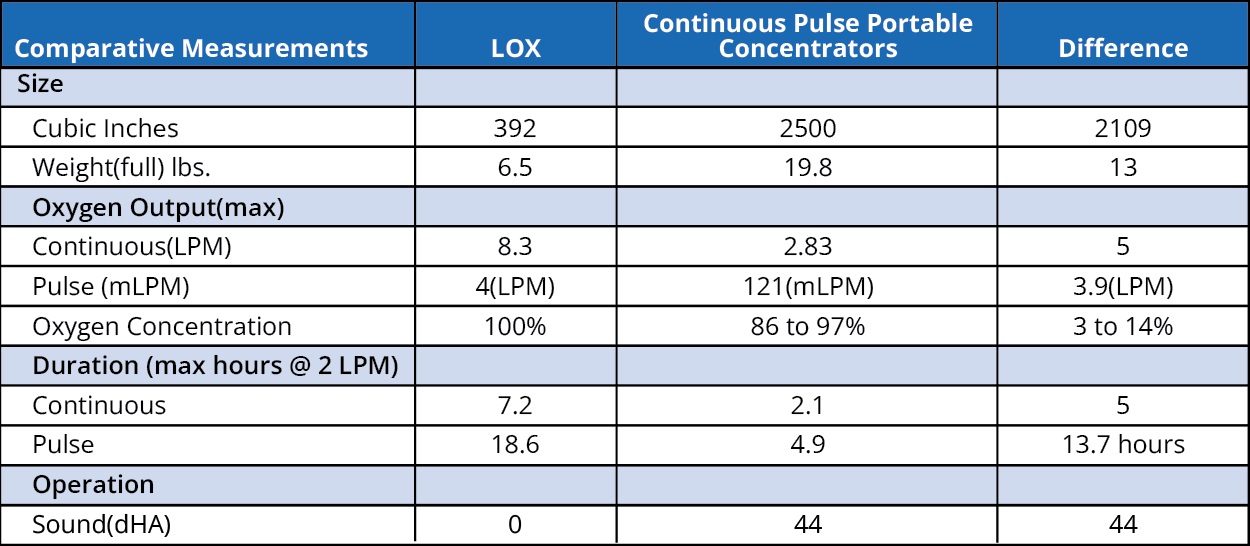
Reproduced below is a comparison chart, displaying the average characteristics for LOX vs. continuous/pulse flow portable oxygen concentrators. This chart is from a review by Burt Cancaster entitled "Liquid Oxygen Therapy" that details medical liquid oxygen and compares LOX with oxygen concentrators.
Additional LOX Resources
-
 Liquid Oxygen Review and Comparison with Oxygen Concentrators detailed description of the advantages and disadvantages of LOX.
Liquid Oxygen Review and Comparison with Oxygen Concentrators detailed description of the advantages and disadvantages of LOX.






Login and Registration Form