Who Uses This Product? Individuals who need to be fed enterally directly to the jejunum who do not want a feeding tube to disrupt their daily lives more than it has to.
Why They Love This Product: The MIC-KEY GJ Tube has a low-profile feeding port that is smaller than the percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy (PEG) tube. The port sits close to the skin and doesn't need to be taped in place. It won't snag on clothing or pull during day-to-day activities.
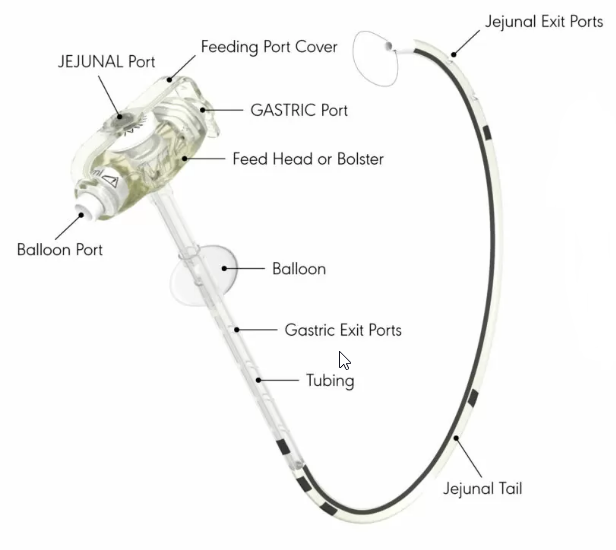
MIC KEY GJ Tube Overview
The MIC-KEY Low Profile Gastric-Jejunal Tubing is a gastrostomy-jejunostomy feeding tube that goes through the wall of the stomach and into the small intestine to allow for enteral feeding. It is commonly referred to as a Gastric-Jejunal tube. The MICKEY GJ Tube has a feeding port that sits close to the skin. It does not require any tape or dressing to cover and secure it into place. The low-profile design means the port won't snag on clothing or accessories, won't pull or catch during daily activities, and can easily be concealed beneath clothing.
Bypassing the stomach for feeding is sometimes necessary for some patients. The Gastro-jejunal tubing threads into the jejunal (J) portion of the small intestine. This type of tubing has separate ports to access both the stomach (G port) and the small intestine (J port), though some tubes, often called Transjejunal (TJ) tubes, only allow access to the small intestine. This tubing serves patients who are at high risk for aspiration since feedings through the jejunal port are less likely to be regurgitated backward past the pylorus.
Features and Benefits
- Low-Profile Design Is Easy To Conceal
- SECUR-LOK Feature Locks Feeding Tube in Place
- Sits at Skin Level -- Reduces Interference With Clothing
- Medical-Grade Silicone Construction Less Likely To Be Rejected by the Body
- Silicone Retention Balloon Eliminates Buried Bumper Syndrome
- Available in Multiple French and Stoma Sizes To Fit Most Adults
- Available With EnFit and Non-EnFit Connectors
- Anti-Reflux Valve Keeps Gastric Fluids From Leaking Out
- Latex-Free and Sterile
- Port for Food, Medication, and Balloon Inflation
- Ports Are Clearly Marked for Ease of Use
The MIC KEY Difference
The MIC-KEY Avanos GJ Tube is different from percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy (PEG) tube in that the feeding port is low-profile and sits close to the skin. Typically, the PEG tube hangs loosely from the stoma and needs to be taped in place or covered. In comparison, the MIC-KEY Low Profile Gastric-Jejunal Tube protrudes from the stoma and sits flat against it. Without a long cord to get in the way, there is little chance of snagging the port on clothing, bags, or other objects during daily activities. Patients can live their lives without worrying about whether or not their movements will tug on or displace their Gastric-Jejunal tube.
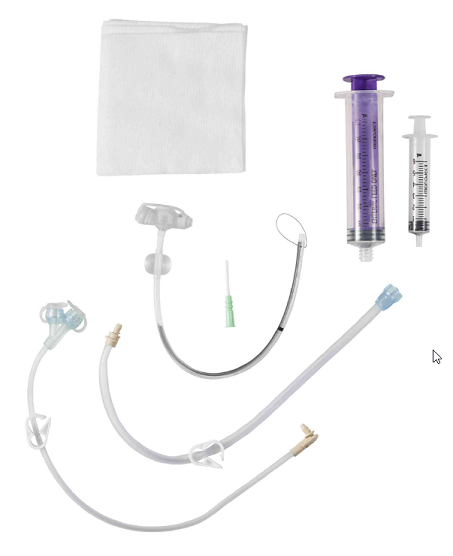
What Comes in the Box?
- MIC-KEY low-profile feeding gastric-jejunal tube
- Introducer cannula
- MIC-KEY Standard extension set with SECUR-LOK right angle connector
- 2 MIC-KEY ENFit feeding connectors
- MIC-KEY bolus extension set with ENFit feeding connector, SECUR-LOK straight connector
- 6-milliliter luer-slip syringe
- 35-milliliter female ENFit syringe
- 4 gauze pads
- Directions for use
- Patient care guide
Selection Components
There are several options when it comes to choosing the correct MIC-KEY Gastric-Jejunal Tube. If the correct tube is not placed, there could be complications.
- French Size. All G-tubes and Gastric-Jejunal tubes are sized by the width of the tube using the French scale. This number represents the diameter of the tube.
- Stoma Size. This number represents the length of the stoma tube.
- Jejunal Length. This number represents the length of the tube that extends into the jejunal of the small intestines.
- Balloon Volume. This is the size of the balloon that keeps the Gastric-Jejunal tube secured in place.
- Connection. The MIC-KEY Low Profile Gastric-Jejunal Tube is available with an ENFit connector or a Non-ENFit connector. ENFit connectors meet international connection standards.
How To Use
The MIC-KEY Gastric-Jejunal Tube has three ports:
- One for the stomach to administer medication or to vent air out.
- One for the tube that goes to the small intestines for feeding.
- One to inflate or deflate the silicone balloon.
How To Feed
Please note that a Gastric-Jejunal tube is not eligible for bolus feeding. Because the Gastric-Jejunal tube extends into the small intestines and the small intestines can't handle large amounts of liquid quickly, the formula must be trickled in over long periods of time.
Continuous feeding uses a and a portable The pump provides formula at a set rate. Healthcare professionals may have recommendations for what pump is best for individual patients' situations.
Needed Equipment:
- The extension set
- Liquid food
- A clean feeding bag
- A feeding pump
- 5- to 10-milliliter syringe (for flushing)
- Room-temperature water (for flushing)
Setting Up the Mic Key Low Profile Gastric-Jejunal Tube
- Wash hands with soap and water.
- Be certain the feeding pump is in the stop/off mode and that the clamp on the feeding bag tube is closed.
- Check the label and expiration date of the liquid food. It is not recommended that food past its expiration date be used. Instead, get a new bag or can of food.
- Pour a little more than the prescribed amount of liquid food into the feeding bag. Hang the bag above the pump. Make sure the feeding bag tubing hangs straight.
- Prime the Mic Key Gastric-Jejunal Tube to remove any air. Do this by opening the clamp and slowly letting a small amount of formula through the end of the feeding bag tube.
- Engage the clamp on the feeding tube bag.
Feeding
- Load the feeding bag tube into the pump.
- Open the feeding port cap. Make sure the clamp on the extension tube is engaged. Line up the extension tube with the MIC-KEY feeding port and rotate clockwise to lock it in place.
- Connect the feeding bag tube to the other end of the extension tube.
- Disengage the clamps on the feeding tube and the extension tube.
- Ensure the pump settings are correct, then turn on the pump to begin feeding.
When Finished
- Disconnect the feeding bag tubing from the extension tubing. With the larger syringe, flush the extension tube with water to clear the remaining formula. Flush the extension set until the tube is clear. Disconnect the syringe.
- Unlock the extension tube by rotating it counter-clockwise until the black line on the extension tube lines up with the line on the feeding port. Gently remove the extension set and cap the MIC KEY Gastric-Jejunal tube.
- Wash the extension set with warm, soapy water until the tube is clear. Rinse thoroughly with clear water. 1
When To Seek Medical Attention
In the case of accidental displacement, the GJ Tube MIC KEY must be replaced by a licensed medical professional. If the tube is displaced for any reason, it cannot be put back in like a regular G-tube. Contact a medical professional as soon as possible.
Signs the tube has made its way up into the stomach
- Vomiting formula
- Gagging and retching
- Abdominal discomfort or pain
- Bloated stomach
- Diarrhea
- Leaking of formula from the stoma
Contact a Medical Professional If the Following Occurs:
- The Gastric-Jejunal tube becomes displaced.
- The stoma is bleeding.
- The stoma is persistently red or sore.
- There is an odor.
- The skin around the stoma is swollen.
- There is pus around the stoma.
- There is consistent pain or a fever.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a gastrostomy-jejunostomy tube?
It is a tube that goes through the stomach and into the small intestine.
Why use a Gastric-Jejunal tube?
A Gastric-Jejunal tube is implanted when a patient has trouble keeping food down when it's introduced to the stomach.
What is the difference between a G-tube and a Gastric-Jejunal tube?
A G-tube extends into the stomach and allows feeding to be done enterally. Formula goes straight into the stomach, bypassing the mouth. Similarly, a Gastric-Jejunal tube extends into the stomach but also into the small intestine (or jejunum), allowing formula to bypass the stomach. This type of tube is necessary when feedings cannot be safely let into the stomach on its own. A Gastric-Jejunal tube is typically used for longer periods of enteral feeding.
What is the difference between the MIC Gastric-Jejunal tubing and the MIC KEY Low Profile Gastric-Jejunal Tube?
The MIC Gastric-Jejunal tubing has a length of tubing that hangs outside the body. The MIC-KEY Gastric-Jejunal tubing has a low-profile design that sits close to the skin and doesn't need to be secured in place.
How often should Gastric-Jejunal feeding tubes be replaced?
Approximately every three months. Medical professionals will typically discuss this with the patient when the tube is implanted.
A Formula For Every Occasion
The feeding port on the MIC Gastric-Jejunal Tube allows medication or to be delivered directly into the small intestines via a feeding tube. Vitality Medical offers a variety of tube feeding formulas for adults and children.
- is formula specifically for children from 1 to 13 years old.
- is a unique carb and fat blend that provides 24 essential vitamins and minerals.
- is made with real food ingredients and meant for patients who want a real food component to their tube feeding.
Cleaning and Care Tips
Keeping the MIC-KEY Low-Profile Gastric-Jejunal tubing and the skin around it clean is just as important as the feeding process. The tube itself and the area (stoma) around it should be kept clean and dry.
Cleaning the Low-Profile Gastric-Jejunal Tube
The MIC Gastric-Jejunal Tubing and the skin around and under it should be cleaned once a day. Be sure to wash hands before touching the Gastric-Jejunal tube. Cleaning can be done with water and mild soap along with a tissue or cotton-tip applicator.
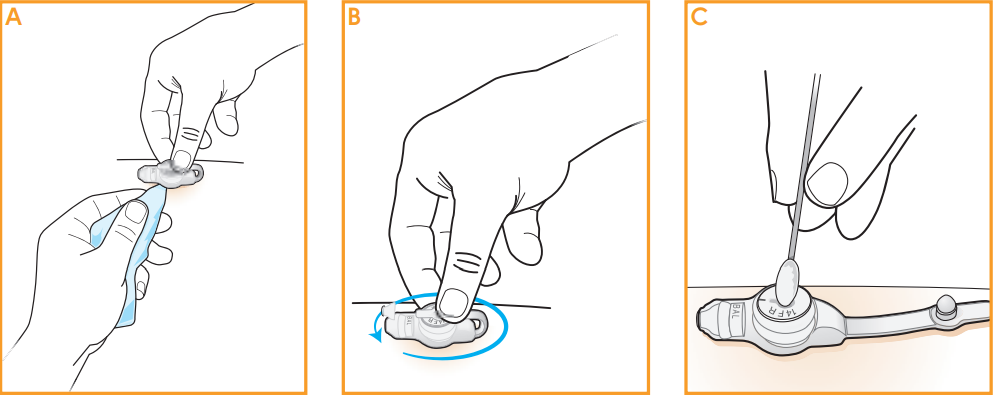
Note: The extension set should be replaced at least once every two weeks for better functionality and hygiene.
Cleaning the Feeding and Extension Tube
- Wash hands before touching the tube.
- Wash the extension set with warm, soapy water until the tube is clear. Rinse thoroughly with clear water.
Specifications
- Manufacturer: Avanos
- Brand: MIC-KEY
- Tube Tip Type: Tapered Distal Tip
- French Sizes: 16, 18, 22
- Stoma Lengths (Centimeters): 1.2, 1.5, 1.7, 2.0, 2.3, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5
- Jejunal Tube Lengths (Centimeters): 15, 22, 30, 45
- Balloon Volume: 3 to 5 Milliliters, 7 to 10 Milliliters
- Connection Types: EnFit and Non-EnFit
- Material: Medical-Grade Silicone
- Application: Enteral Feeding Tube
- Product Numbers: BLD02501622, BLD0270161015, BLD0270161022, BLD0270161215, BLD0270161230, BLD0270161515, BLD0270161530, BLD0270161722, BLD0270161730, BLD0270162022, BLD0270162030, BLD020163545, BLD0270181230, BLD0270181522, BLD0270182022, BLD0270182030, BLD0270182330, BLD0270182530, BLD0270182545, BLD0270183045
Related MIC-KEY Products
- - Bolus and Non-Bolus Options, 12 or 24 Inch Length.
- - Silicone 14 and 18 French with 1.0 to 4 cm length.
- - Tapered or Recessed Distal, 12 to 24 French Sizes, and 0.8 to 5.0 cm Length.
- - Trimable Distal Tip, 14 or 18 French Size 1.0 to 4.0 Stoma Size.
- - Tapered Distal Tip, Dual Exit Ports, 14 to 24 French Size.
- - Built-in Medicine Port, Non-Recessed Distal Tip, Dual Exit Ports, 12 to 30 French Size.
- - determines correct feeding tube shaft length.
Product Videos
Life With the MIC-KEY Low Profile Feeding Tube (10:25 minutes)
MIC Gastric-Jejungal Tube Maintenance and Stoma Care (3:15 minutes)
Footnotes
- 1Gastrostomy or Gastro-jejunum Tube: Pump Feeding. Saint Luke's. (n.d.). https://www.saintlukeskc.org/health-library/gastrostomy-or-gastro-jejunum-tube-pump-feeding. (Last Accessed 7/30/2021)


Login and Registration Form